There are 2 Ways to prescribe AMPYRA
ePrescribe AMPYRA in 2 simple steps
Find and select Pacific LTC Pharmacy in your EMR by searching one of the options below:

Fax:
949-524-3566
(Recommended)
NCPDP:
5664417
NPI:
1871002485
Include the patient's current mobile phone number.*
Address:
361 Hospital Rd. Ste 425
Newport Beach, CA 92663
Chart notes and additional information

Fax chart notes or other information to (844) 317-5359


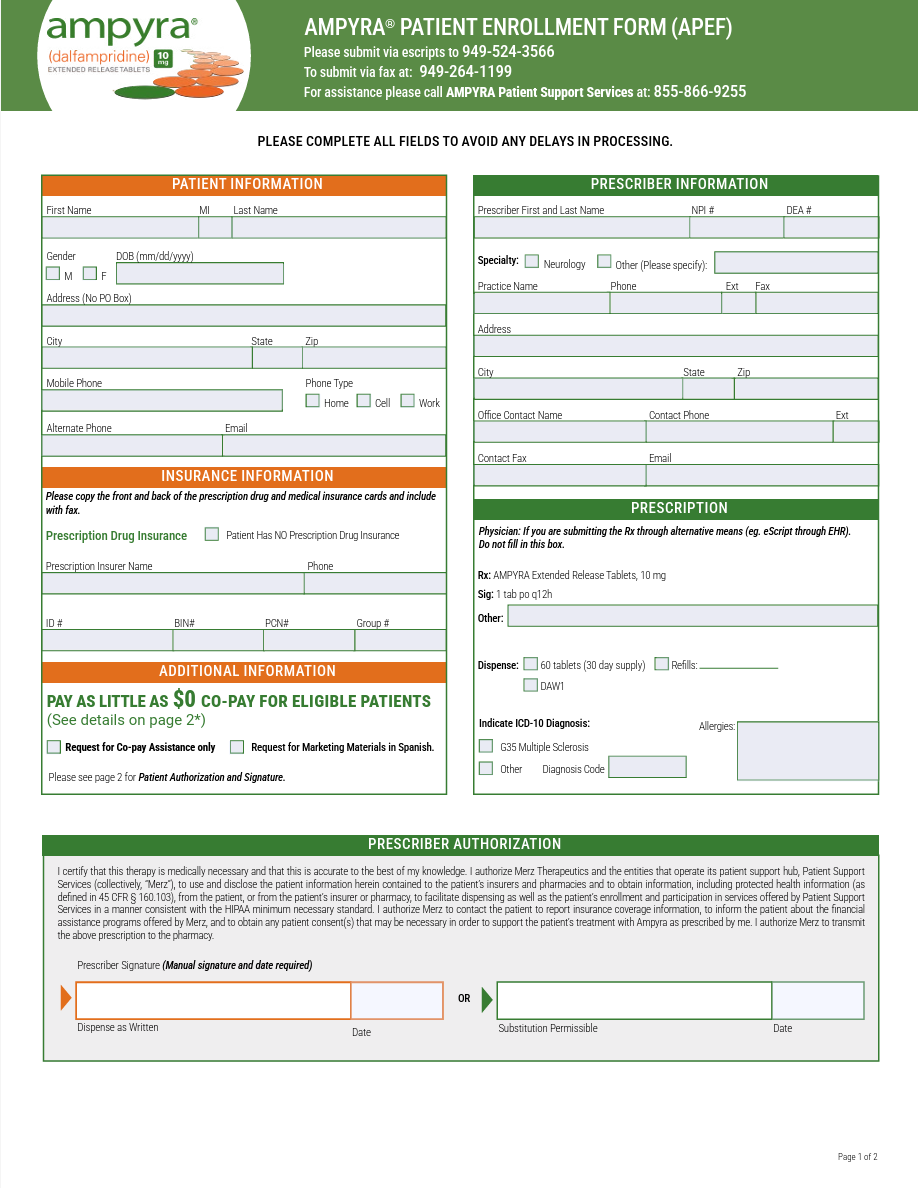
Complete the Patient Enrollment Form(Formerly known as Service Request Form)
FILL OUT FORM

Download and fill out a Patient Enrollment Form
Fax

Fax completed form to 1-949-264-1199
If you do not have access to a fax machine, call us at 1-855-866-9255.
*You may receive a phone call from an AMPYRA patient support specialist if additional information is required to initiate prior authorization.
†Standard text and data rates may apply.
EMR, electronic medical record.
Indication
AMPYRA® (dalfampridine) Extended Release Tablets, 10 mg, is indicated to improve walking in adults with multiple sclerosis (MS). This was demonstrated by an increase in walking speed.
Important Safety Information
AMPYRA is contraindicated in patients with history of seizure, moderate or severe renal impairment (CrCl ≤ 50 mL/min), or history of hypersensitivity to AMPYRA or 4-aminopyridine.
Indication
AMPYRA® (dalfampridine) Extended Release Tablets, 10 mg, is indicated to improve walking in adults with multiple sclerosis (MS). This was demonstrated by an increase in walking speed.
Important Safety Information
- AMPYRA is contraindicated in patients with history of seizure, moderate or severe renal impairment (CrCl ≤ 50 mL/min), or history of hypersensitivity to AMPYRA or 4-aminopyridine.
- AMPYRA can cause seizures. The risk of seizures increases with increasing doses. Permanently discontinue AMPYRA if seizure occurs. In the post-marketing period seizures have been reported. The majority of seizures occurred at the recommended dose, in patients without a history of seizures, and generally within days to weeks of starting therapy.
- AMPYRA has not been evaluated in patients with history of seizures or with epileptiform activity on an EEG, as these patients were excluded from clinical trials. The risk of seizures in patients with epileptiform activity on an EEG is unknown, and could be substantially higher than that observed in clinical studies.
- Avoid concomitant use of AMPYRA with other forms of 4-aminopyridine (4-AP, fampridine), since the active ingredient is the same. Instruct patients to discontinue use of any product containing 4-AP prior to initiating AMPYRA to reduce the potential for dose-related adverse reactions.
- AMPYRA can cause anaphylaxis and severe allergic reaction. Signs and symptoms included respiratory compromise, urticaria, and angioedema of the throat or tongue. If an anaphylactic or other serious allergic reaction occurs, permanently discontinue AMPYRA.
- AMPYRA is cleared predominantly by the kidneys. The risk of seizures in patients with mild renal impairment (CrCl 51–80 mL/min) is unknown, but AMPYRA plasma levels in these patients may approach those seen at a dose of 15 mg twice daily, a dose that may be associated with an increased risk of seizures. Estimated CrCl should be known before initiating AMPYRA and monitored at least annually during treatment.
- The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 2% and at a rate greater than placebo) for AMPYRA in MS patients were urinary tract infection, insomnia, dizziness, headache, nausea, asthenia, back pain, balance disorder, MS relapse, paresthesia, nasopharyngitis, constipation, dyspepsia, and pharyngolaryngeal pain.
- The risk of adverse reactions, including seizures, increases with increasing AMPYRA doses. There is no evidence of additional benefit at doses greater than 10 mg twice daily.
- Concomitant use with OCT2 inhibitors (e.g., cimetidine) may cause increased exposure to AMPYRA and potential risk of seizures.
- There are no adequate data on AMPYRA in pregnant women. Based on animal data, use of AMPYRA during pregnancy may cause fetal harm.
- There are no data on presence of AMPYRA in breastmilk; benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with benefit of AMPYRA to the mother and potential risks to the infant.
- Safety and effectiveness of AMPYRA in patients younger than 18 years have not been established.
- Clinical studies of AMPYRA did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, it is important to know the estimated CrCl before initiating AMPYRA.
Please see the Full Prescribing Information.

 Patient Enrollment Form
Patient Enrollment Form